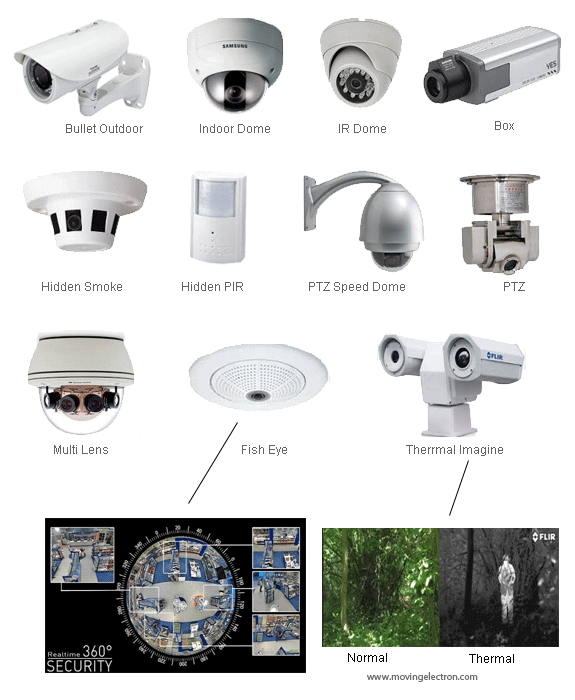
Have you ever wondered about the different types of security camera lenses? If so, you’re in luck! This article is here to shed some light on the topic and help you understand the various options available. Whether you’re looking to enhance the security of your home or business, it’s important to choose the right lens for your needs. By exploring the different types, you’ll gain a better understanding of how they can impact image quality, field of view, and overall surveillance capabilities. So, get ready to dive into the world of security camera lenses and discover what makes each type unique.
Fixed Focal Length Lenses
Definition
Fixed focal length lenses, also known as prime lenses, have a fixed focal length and cannot be adjusted. They have a constant angle of view, meaning that the field of view is fixed. These lenses are designed to capture images at a specific focal length, which can range from wide-angle to telephoto.
Benefits
One of the key benefits of fixed focal length lenses is their superior image quality. Due to their simpler optical design and lack of movable elements, these lenses are often able to produce sharper and more detailed images compared to zoom lenses. They are also generally faster, meaning they have wider maximum apertures, allowing them to capture more light and perform better in low-light conditions.
Another advantage of fixed focal length lenses is their compact and lightweight nature. With fewer components, these lenses are often smaller and more portable, making them ideal for travel photography or when you need to pack light. Additionally, their fixed focal length encourages photographers to be more creative and intentional with their compositions, as they need to physically move closer or further from the subject to frame the shot.
Drawbacks
One major disadvantage of fixed focal length lenses is their lack of flexibility. Unlike zoom lenses, you cannot adjust the focal length to zoom in or out, meaning you need to physically move closer or further from the subject to compose your shot. This can be inconvenient in certain situations, such as when photographing wildlife or events where you may not have control over your subject’s distance.
Additionally, the limited focal length of fixed focal length lenses means they may not be suitable for all types of photography. For example, a wide-angle prime lens may not provide the reach needed for capturing distant subjects, while a telephoto prime lens may not be ideal for capturing wide landscapes.
Applications
Fixed focal length lenses find their applications in various genres of photography. Wide-angle prime lenses, typically with focal lengths below 35mm, are popular for landscape, architectural, and street photography, allowing you to capture expansive scenes with a broad perspective. Portrait photographers often opt for medium telephoto prime lenses, around 85mm, which offer a flattering compression and beautiful bokeh for stunning portrait shots.
Photographers who prioritize image quality and low-light performance may choose fixed focal length lenses with larger maximum apertures. These wide-aperture primes are particularly well-suited for indoor or low-light situations, such as event photography or astrophotography. Their ability to gather more light can result in sharper images with less noise.
In summary, fixed focal length lenses offer exceptional image quality, portability, and the opportunity to develop creative compositions. While they may lack the versatility of zoom lenses, they excel in specific applications and are a valuable tool for many photographers.
Varifocal Lenses
Definition
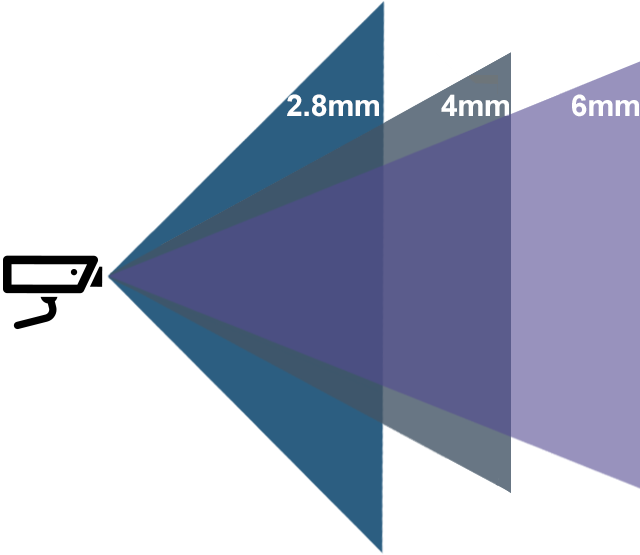
Varifocal lenses, also known as zoom lenses, allow you to adjust the focal length within a certain range. These lenses provide the flexibility to zoom in or out, allowing you to frame your shots without physically moving closer or further from the subject.
Benefits
One of the primary advantages of varifocal lenses is their versatility. By adjusting the focal length, you can quickly switch between different types of shots without having to change lenses. This makes them well-suited for situations where you need to capture a variety of subjects and distances, such as travel photography or event coverage.
The ability to zoom also allows you to stay in one position, which can be advantageous in certain scenarios. For example, when photographing wildlife, you can maintain a safe distance while still filling the frame with your subject. This is particularly useful for capturing elusive or skittish animals.
Drawbacks
One drawback of varifocal lenses is their typically larger size and weight compared to fixed focal length lenses. The inclusion of movable elements to adjust the focal length adds complexity and bulk to the lens, making them less portable. This can be a consideration for photographers who value lightweight and compact gear, such as hikers or documentary photographers constantly on the move.
Another potential drawback of varifocal lenses is their potentially slower maximum aperture compared to some prime lenses. As the focal length increases, the maximum aperture typically decreases, limiting their low-light performance. This can result in slower shutter speeds or increased ISO settings, which may introduce more noise into the image.
Applications
Varifocal lenses are widely used in various photography genres due to their versatility. They are commonly found in kits for beginners or enthusiasts, as their zoom range allows for a wide range of shooting possibilities without the need to invest in multiple prime lenses.
Photographers covering sports or wildlife often rely on telephoto zoom lenses to capture distant subjects. These lenses provide the flexibility to zoom in and track the action while maintaining a safe shooting distance. On the other hand, wide-angle zoom lenses are popular for landscape or architectural photography, enabling you to capture sweeping vistas or fit large structures into the frame.
Varifocal lenses are also beneficial in documentary or street photography, where moments may unfold quickly, and you need to react swiftly to capture the shot. The ability to zoom in or out allows you to adjust your framing and composition on the fly, ensuring you don’t miss any crucial moments.
In conclusion, varifocal lenses offer versatility and convenience, making them an essential tool for photographers who need flexibility in framing their shots. While they may sacrifice some image quality and portability compared to fixed focal length lenses, their ability to zoom in and out compensates for these limitations in many situations.
Auto Iris Lenses
Definition
Auto iris lenses are lenses that feature an iris diaphragm that is automatically controlled by the camera or lens system. The iris diaphragm adjusts the amount of light entering the lens, which is crucial for maintaining proper exposure levels in different lighting conditions.
Benefits
One of the significant benefits of auto iris lenses is their ability to adapt to changing light conditions automatically. The camera or lens system measures the amount of light in the scene and adjusts the iris diaphragm accordingly, ensuring that the image is properly exposed. This eliminates the need for manual adjustments or constantly monitoring and adjusting the exposure settings.
Additionally, auto iris lenses offer consistent and accurate exposure throughout a video or surveillance recording. As lighting conditions change, the iris diaphragm can smoothly and seamlessly adjust, resulting in a balanced exposure. This is particularly useful in security camera systems, where reliable and accurate footage is essential for effective surveillance.
Drawbacks
One potential drawback of auto iris lenses is their reliance on the camera or lens system to control the iris diaphragm. If the system malfunctions or loses power, the lens may not be able to adjust the aperture, leading to incorrect exposure. This can be a concern in critical situations where uninterrupted surveillance is necessary.
Another consideration is the cost of auto iris lenses compared to manual iris lenses. The additional technology and mechanism required for automatic aperture control can increase the price of the lens. However, the benefits of precise exposure control and ease of use may outweigh the added cost for certain applications.
Applications
Auto iris lenses are commonly used in video surveillance systems, where optimal exposure is crucial for capturing clear and identifiable footage. They ensure that both bright and low-light areas within a scene are properly exposed, allowing for accurate identification of individuals or monitoring of areas with varying lighting conditions.
These lenses are also used in video production or filmmaking, where consistent exposure is essential for maintaining visual continuity between shots. Auto iris lenses can seamlessly adjust to changes in lighting, whether filming indoors, outdoors, or in rapidly changing environments. This ensures that the footage remains well-exposed and visually pleasing, minimizing the need for manual exposure adjustments during filming.
Overall, auto iris lenses provide reliable exposure control and consistent image quality in a variety of applications. Their automatic adjustment capabilities make them well-suited for scenarios where lighting conditions change frequently, ensuring accurate and dependable footage or images.
Manual Iris Lenses
Definition
Manual iris lenses, as the name suggests, require manual adjustment of the iris diaphragm to control the amount of light entering the lens. These lenses allow the user to manually set the aperture size, offering greater control over the exposure and depth of field.
Benefits
One of the primary benefits of manual iris lenses is the control they provide over the exposure settings. By manually adjusting the aperture, photographers have the freedom to fine-tune the exposure to their liking or match specific shooting conditions. This is particularly useful in situations where creative control and precise exposure are paramount, such as studio photography or portrait sessions.
Manual iris lenses also offer a consistent aperture setting throughout the shoot. Once the aperture is manually set, it remains fixed, ensuring consistent exposure for the duration of the shooting session. This can be advantageous for scenarios where maintaining a consistent exposure is critical, such as product photography or still life compositions.
Drawbacks
The main drawback of manual iris lenses is the need for constant monitoring and adjustment of the aperture settings. As lighting conditions change, you must manually adapt the aperture to maintain accurate exposure, which can be time-consuming and may result in missed shots. This can be a challenge in fast-paced environments or when capturing rapidly changing scenes.
Additionally, the lack of automatic exposure adjustment can be a disadvantage in situations with unpredictable or rapidly changing lighting conditions. For example, in event photography where lighting setups often change, constantly adjusting the aperture manually may not be practical or efficient.
Applications
Manual iris lenses find applications in various genres of photography, particularly those that require precise control over exposure settings. Portrait photographers, for instance, often prefer manual iris lenses to achieve a shallow depth of field, blurring the background and drawing attention to the subject. By manually adjusting the aperture, photographers can fine-tune the level of background blur, creating the desired aesthetic.
These lenses are also well-suited for studio photography, where lighting conditions can be carefully controlled. By manually manipulating the aperture, photographers can achieve consistent and specific exposure levels, which is crucial for accurately capturing products or controlling the lighting ratios in the scene.
In summary, manual iris lenses provide photographers with greater control over the exposure and depth of field, offering the flexibility to achieve specific artistic effects or adapt to challenging lighting conditions. While they require more manual adjustments and constant monitoring, their precise control over exposure makes them a valuable tool for photographers who prioritize creative control.
Wide Angle Lenses
Definition
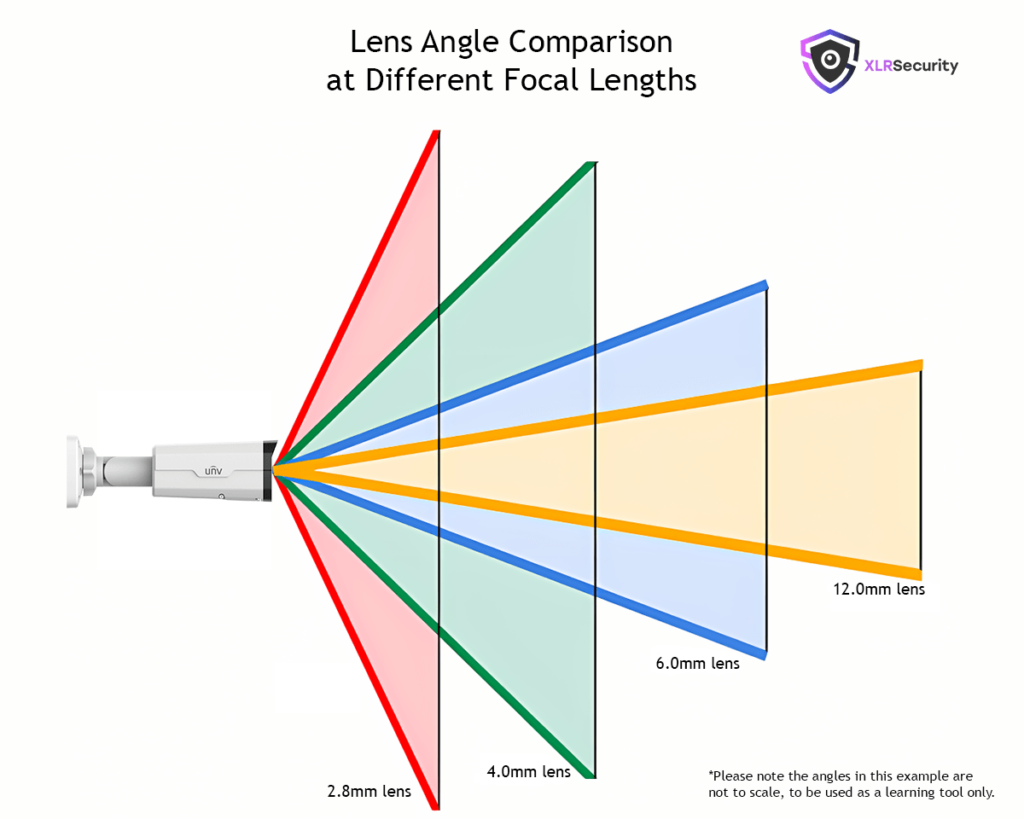
Wide-angle lenses, as the name suggests, cover a wide field of view, enabling you to capture expansive scenes and fit more into the frame. These lenses have a shorter focal length, typically below 35mm, and offer a wider angle of view compared to normal or telephoto lenses.
Benefits
One of the key benefits of wide-angle lenses is their ability to capture vast scenes or architecture in a single frame. Whether you’re photographing a breathtaking landscape or an expansive cityscape, wide-angle lenses allow you to fit more into the frame, showcasing the grandeur and scale of the subject. They provide a sense of space and depth, creating immersive and captivating images.
Wide-angle lenses can also exaggerate perspective, making subjects closer to the lens appear larger while elongating the distance between objects. This effect, often referred to as “foreshortening,” can be creatively utilized to emphasize certain elements or create a unique visual impact. It is frequently used in architectural or interior photography to emphasize the lines and features of buildings or spaces.
Drawbacks
One drawback of wide-angle lenses is the potential distortion, particularly towards the edges of the frame. Due to the wide angle of view, straight lines near the edges of the frame can appear curved, resulting in a phenomenon known as “barrel distortion” or “fish-eye effect.” This distortion can be corrected to some extent in post-processing, but it may still affect the overall image quality and require additional effort to correct.
Another consideration is the potential for a loss of subject isolation and background compression. Wide-angle lenses have a wider depth of field, meaning a larger portion of the scene will be in focus. While this can be advantageous for capturing a sharp image from foreground to background, it may not be ideal for isolating a subject from the background or achieving a shallow depth of field with significant background blur.
Applications
Wide-angle lenses find applications in various photography genres where capturing a broad perspective or emphasizing the scale is desired. Landscape photographers often rely on wide-angle lenses to capture sweeping vistas and convey the vastness and majesty of natural scenery. The ability to include both the foreground and background in sharp focus allows for greater depth and a more immersive composition.
These lenses are also widely used in architectural and interior photography, where they can showcase large structures or expansive living spaces. The wide angle of view helps capture the entire building or room, while specific distortion correction techniques can be employed to minimize any unwanted distortion.
Street photographers can take advantage of wide-angle lenses to capture dynamic scenes with a sense of context. The wide field of view enables them to include the surroundings and environment, providing a broader story for the viewer.
In summary, wide-angle lenses excel at capturing expansive scenes, emphasizing perspective, and providing a broad field of view. While they may introduce some distortion and limit background isolation, their ability to create immersive images make them a valuable tool for various photographic applications.
Telephoto Lenses
Definition
Telephoto lenses have a longer focal length, typically above 70mm, allowing you to capture distant subjects with magnification. These lenses compress the distance between objects, making them appear closer together and bringing far-off subjects into closer view.
Benefits
One of the primary benefits of telephoto lenses is their ability to bring distant subjects closer, making them ideal for sports, wildlife, and any photography where the subject is far away or difficult to access. The magnifying effect allows you to capture details that would be missed with a shorter focal length lens, enabling you to bring the viewer closer to the action or animal behavior.
Telephoto lenses also offer a shallower depth of field, even at smaller apertures, allowing for greater subject isolation from the background. This bokeh effect, where the background appears creamy and blurred, helps draw attention to the subject and creates a pleasing aesthetic.
Drawbacks
One potential drawback of telephoto lenses is their physical size and weight. The longer focal length and increased magnification require larger lens elements, resulting in bulkier and heavier lenses. This can make them more challenging to handle, especially when shooting handheld or in fast-paced situations.
Another consideration is the limited field of view. Telephoto lenses have a narrower angle of view compared to wider lenses, potentially making it more challenging to frame the scene or capture expansive landscapes. This can limit their application in certain genres of photography that require a wider perspective.
Applications
Telephoto lenses are widely used in sports and wildlife photography to capture action and distant subjects. Their ability to bring the viewer closer to the subject allows for detailed and impactful images, whether it’s freezing a split-second moment in a sports game or capturing the behavior of animals in the wild.
Portrait photographers often favor telephoto lenses for their flattering compression and ability to isolate the subject from the background. The shallow depth of field combined with the separation between the subject and the background can create stunning portraits with creamy bokeh, drawing attention to the subject’s features and expressions.
Photographers covering events and concerts can also benefit from telephoto lenses, as they allow them to capture performers or onstage action from a distance while maintaining a safe and unobtrusive shooting position.
In conclusion, telephoto lenses excel in bringing distant subjects closer and providing greater subject isolation. While they may be heavier and have a narrower field of view, their ability to capture details and compress distance make them invaluable for sports, wildlife, and portrait photography and a useful tool in various other genres.
Fish-Eye Lenses
Definition
Fish-eye lenses are ultra-wide-angle lenses with extremely short focal lengths, typically below 10mm. These lenses capture an extremely wide field of view, often exceeding 180 degrees, resulting in a unique and distinct visual perspective.
Benefits
One of the primary benefits of fish-eye lenses is their ability to capture an incredibly wide field of view, offering a truly immersive experience. The distorted, curved perspective creates a unique and exaggerated effect that can be creatively utilized to add a sense of drama or playfulness to the images.
Fish-eye lenses also excel in capturing scenes where the photographer wants to include as much of the surroundings as possible. Whether photographing architecture, landscapes, or extreme sports, these lenses can showcase the expansive environment and add a dynamic element to the composition.
Drawbacks
The main drawback of fish-eye lenses is the significant distortion they introduce to the image. The curved and distorted lines near the edges of the frame can result in a “fish-eye effect,” where straight lines appear bent or curved. While this distortion can be artistically appealing in some cases, it may not be desired or suitable for every type of photography.
Due to the ultra-wide-angle nature of fish-eye lenses, there is usually a loss of subject detail towards the edges of the frame. Straight lines and objects near the edges may be heavily distorted and lose sharpness, resulting in a reduction in overall image quality. This can be a consideration for photographers looking for precise and distortion-free images.
Applications
Fish-eye lenses are commonly used in various genres of photography where the unique distortion and ultra-wide perspective can enhance the creative impact of the image. They are popular in architectural photography, as the exaggerated lines and perspective can highlight the grandeur and distinctive features of buildings.
Landscape and nature photographers often utilize fish-eye lenses to capture sweeping vistas or incorporate the sky and surrounding elements into the composition. The wide field of view and distortion can create a sense of depth and add an extra element of interest to the images.
In action sports or extreme photography, fish-eye lenses can capture the subject and the surrounding environment in a single frame, providing a unique and immersive visual experience. The wide perspective adds impact and intensity to the images, creating a sense of being right in the heart of the action.
In summary, fish-eye lenses offer a distinct and dramatic perspective, allowing photographers to explore creative possibilities and capture images with an immersive and dynamic feel. While the distortion and potential loss of image quality are considerations, their ability to provide an ultra-wide field of view makes them a valuable tool for photographers seeking to push the boundaries of visual storytelling.
Pinhole Lenses
Definition
Pinhole lenses, as the name suggests, do not have a traditional lens system. Instead, they use a tiny pinhole aperture to create a photo. Light passes through the small opening and projects an inverted image onto the camera’s image sensor or film.
Benefits
One of the key benefits of pinhole lenses is their simplicity. With no lens system to worry about, these lenses are often small, lightweight, and easy to use. This makes them portable and ideal for situations where you want a simple and uncomplicated photography experience.
Pinhole lenses also offer a unique and dream-like image quality. The absence of a traditional lens system and the small aperture creates a soft and ethereal look, with a high depth of field and diffused light. This can result in images with a certain romantic or nostalgic quality, adding a touch of artistic charm to your photographs.
Drawbacks
One potential drawback of pinhole lenses is their limited light-gathering abilities due to the small aperture size. This means longer exposure times are often required, making them less suitable for capturing fast-moving subjects or shooting in low-light conditions without the aid of a tripod.
The absence of a traditional lens can also result in significant image distortion, particularly towards the edges of the frame. The lack of optical correction leads to a “pincushion distortion” effect, where straight lines appear bowed inwards or barrel distortion, depending on the design. While this distortion can be creatively appealing, it may not be desired or suitable for all types of photography.
Applications
Pinhole lenses find their applications in artistic and experimental photography. They allow photographers to explore alternative image-making processes and let go of traditional sharpness and definition, creating more evocative and abstract images.
These lenses are often popular among practitioners of toy camera or lo-fi photography. Their unique optical properties and dreamy quality can enhance the feeling of nostalgia or playfulness in the images. Additionally, the simplicity and portability of pinhole lenses make them a great option for those who enjoy the process of photography without the technicalities of lenses and complex camera systems.
In summary, pinhole lenses offer a simplified and artistic approach to photography, allowing for a certain degree of unpredictability and creativity. While their limited light-gathering abilities and potential image distortion are considerations, their unique softness and dream-like quality make them a valuable tool for those seeking to experiment and push the boundaries of traditional image-making.
Infrared (IR) Lenses
Definition
Infrared (IR) lenses are specifically designed to capture light in the infrared spectrum, which is invisible to the human eye. These lenses have coatings or filters that block visible light while allowing infrared light to pass through, resulting in unique and striking images.
Benefits
One of the primary benefits of infrared lenses is their ability to capture a different reality. By highlighting the infrared light that is normally invisible to us, these lenses allow photographers to create surreal and otherworldly images. Foliage appears white, skies can turn dark, and infrared wavelengths interact with different materials in unexpected ways, resulting in a unique visual experience.
Infrared lenses also offer the advantage of being able to photograph in unique lighting conditions. Infrared light is abundant, even in low-light situations, allowing for photography in challenging environments where visible light may be limited. This can open up new creative opportunities, particularly in landscape or architectural photography, where unusual lighting conditions can add drama and impact to the image.
Drawbacks
One drawback of infrared lenses is their specialized nature, which can limit their versatility. The infrared effect is not suitable for every type of subject or scene, and it may not yield desirable results for certain genres of photography. Additionally, the specific requirements of infrared photography, such as the need for longer exposures or the necessity of converting the camera for dedicated infrared capture, can add complexity and cost to the process.
Another consideration is the potential for image artifacts or sensor flare. Infrared light interacts differently with camera sensors compared to visible light, which can result in hotspots, lens flares, or unwanted artifacts in the image. Post-processing may be required to correct or minimize these issues, adding extra time and effort to the workflow.
Applications
Infrared lenses find applications in various genres of photography, particularly those that benefit from a surreal or otherworldly look. Landscape photographers often use infrared lenses to capture striking and ethereal scenes, where foliage appears white and skies take on a dark and dramatic tone. The unique lighting and tonal effects of infrared photography can add a sense of mystery and enchantment to familiar landscapes.
Architectural photographers may choose to incorporate infrared lenses to create a distinct and visually impactful image of structures or cityscapes. The infrared light can reveal different textures, surfaces, and materials that are not visible to the human eye, resulting in a fresh and captivating perspective.
Infrared lenses are also used in scientific and technical applications, such as thermal imaging or surveillance. The ability to capture infrared light can provide critical information in various fields, including environmental analysis, security monitoring, or medical diagnostics.
In conclusion, infrared lenses offer a unique and artistic approach to photography, enabling photographers to capture a different reality and reveal unseen aspects of the world. While they may require specialized techniques and additional post-processing, the surreal and otherworldly images they produce make them a powerful tool for those seeking to explore the unseen and push the boundaries of visual storytelling.
Zoom Lenses
Definition
Zoom lenses, also known as varifocal lenses, offer the ability to adjust the focal length within a certain range. These lenses provide flexibility to zoom in or out, allowing you to frame your shots without physically moving closer or further from the subject.
Benefits
One of the primary benefits of zoom lenses is their versatility. By adjusting the focal length, you can quickly switch between different types of shots without having to change lenses. This makes them well-suited for situations where you need to capture a variety of subjects and distances, such as travel photography or event coverage.
The ability to zoom also allows you to stay in one position, which can be advantageous in certain scenarios. For example, when photographing wildlife, you can maintain a safe distance while still filling the frame with your subject. This is particularly useful for capturing elusive or skittish animals.
Drawbacks
One drawback of zoom lenses is their typically larger size and weight compared to prime lenses. The inclusion of movable elements to adjust the focal length adds complexity and bulk to the lens, making them less portable. This can be a consideration for photographers who value lightweight and compact gear, such as hikers or documentary photographers constantly on the move.
Another potential drawback of zoom lenses is the compromise in image quality compared to prime lenses. The complexity of the lens design and the range of focal lengths can result in slightly reduced sharpness and contrast. While the advancements in lens technology have minimized these differences, dedicated prime lenses often offer superior image quality and performance in specific focal lengths.
Applications
Zoom lenses find applications in various photography genres due to their versatility. They are commonly found in kits for beginners or enthusiasts, as their zoom range allows for a wide range of shooting possibilities without the need to invest in multiple prime lenses.
Photographers covering sports or wildlife often rely on telephoto zoom lenses to capture distant subjects. These lenses provide the flexibility to zoom in and track the action while maintaining a safe shooting distance. On the other hand, wide-angle zoom lenses are popular for landscape or architectural photography, enabling you to capture sweeping vistas or fit large structures into the frame.
Zoom lenses are also beneficial in documentary or street photography, where moments may unfold quickly, and you need to react swiftly to capture the shot. The ability to zoom in or out allows you to adjust your framing and composition on the fly, ensuring you don’t miss any crucial moments.
In conclusion, zoom lenses offer versatility and convenience, making them an essential tool for photographers who need flexibility in framing their shots. While they may sacrifice some image quality and portability compared to prime lenses, their ability to zoom in and out compensates for these limitations in many situations.